Armyworm in Corn
Armyworm
Description
Larvae of the true armyworm are greenish brown with a narrow, mid-dorsal stripe and two orange stripes along each

Armyworm
University of KY IPM
side. The yellowish head of the larva is honeycombed with dark lines. Armyworm larvae are about 1.5 inches long when full grown. Pupation occurs in the soil. Adult moths are nocturnal with a small, white dot in the center of each wing.
Damage
Armyworm larvae feed at night and damage corn by stripping the leaves and feeding in the whorl which may destroy the bud. Armyworms generally appear in Kentucky corn in early season, Mid-May through June. Infestations usually develop in small grains or other grass cover crops and in corn, infestations may develop throughout no-till corn following grains or grass crops. The larvae are most often found in luxuriant or lodged vegetation in low wet areas, and cool, wet springs will favor armyworm development. Armyworms are primarily leaf feeders; however, they will feed on awns and tender kernels. Other hosts of armyworms include wheat, bluegrass, oats, rye, and some forages. Remember: Larvae hide under debris or on the ground during the day and feed on the plant at night.
Armyworm Activity in Corn
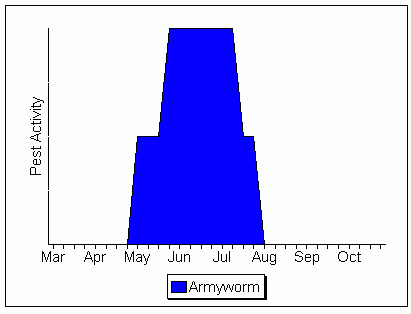
Please note: These dates are approximations only. This calendar was constructed using data from Kentucky, USA. These dates may not apply in your area. You may wish to contact your county extension agent or agricultural consultant for information tailored to your locality.
IPM Techniques and Scouting Procedures
- Scouting is recommended in Kentucky from the time the corn emerges until the plants are waist-high.
- Field edges should be checked first. If armyworms are present, check 20 plants per location and rate feeding damage (0-3).
- Check leaves for signs of damage and examine the ground for dark fecal droppings. Armyworms feed during late afternoon, night and early morning, starting at the edge of a leaf and feeding in towards the midrib. During the day armyworms will often hide under surface litter or in soil cracks.
- Examine 20 plants per location. Select sample sites so that the entire field is covered. Use a 4 foot X 4 foot square to sample each site. You will want to record the number of armyworms present in each 4 X 4 area and the average length of the armyworms. The economic threshold is an average of 16 1/2-inch to 3/4-inch long armyworms per four square foot sample.
- When observing larvae check for parasitic eggs just behind the head. These small, oval, yellow eggs are of a fly parasite that will kill the larva. Avoid treating with insecticides when large numbers of larvae are parasitized.
- Pheromone traps are available for monitoring adult armyworm activity. ENT-54-contains a list of vendors for the lures. The "Texas" wire cone trap is recommended for adult monitoring.
- The economic threshold using plant damage is 35% or more of plants in field are infested and larvae average 1/2 to 3/4 inch long, or 50% or more defoliation is seen on damaged plants.
References and Additional Information
- IPM-2 Kentucky IPM Manual for Corn
ENTFACT 112 - Using Pheromone Traps in Field Crops


