Soybean Podworm
Soybean Podworm
Description
Soybean podworm and Corn earworm are two names for the same insect. Young larvae are very small and grow to

Soybean podworms
University of Kentucky Dept. Entomology
1-1/2 inches in length when full grown. They are usually tan to pale green in color with several dark stripes down the back. Color may vary greatly with some appearing almost black.
Damage
The soybean podworm feeds mainly on pods but may also feed on leaves, stems, and flowers. Larvae will eat the pod wall and consume the seed.
IPM Techniques and Scouting
- Soybean fields using narrow row spacing form a complete canopy sooner, so they are less attractive to egg-laying moths.
- Delayed maturity may also increase the risks of late-season damage. More severe damage tends to be present when large larvae are present on plants with fairly mature pods. This is because the larvae will now feed on the beans inside the pods rather than foliage.
- Sampling for the soybean podworm should be made using a shake cloth. At each sample site, using a two foot cloth, bend the plants over the cloth and shake them vigorously. Note the number of larvae in a four foot sample area at each site. The number of sites you need to examine in a field is based on the size of the field.
- The economic threshold for soybean podworm is two worms(caterpillars) per row foot.
Soybean Podworm Activity
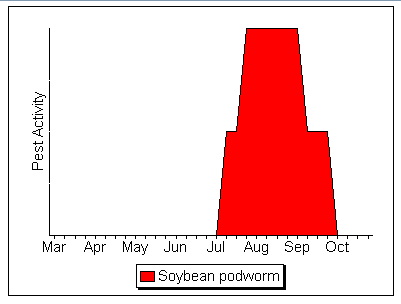
Please note: These dates are approximations only. This calendar was constructed using data from Kentucky, USA. These dates may not apply in your area. You may wish to contact your county extension agent or agricultural consultant for information tailored to your locality.
References and Additional Information
- IPM -3 Kentucky IPM Manual for Soybeans
- Illinois Field Crop Scouting Manual
- Purdue University - Field Crops Pest Management Manual
- Handbook of Soybean Insect Pests by Leon G. Higley and David J. Boethel, Entomological Society of America


